事情起因是这样子,我有个genbank文件,里面记录的是线粒体的注释的坐标信息。由于这个注释是来源同源注释,可能存在错误,因此还需要后续的手动修改。我没去找到专门的工具,只是根据分析结果,手动改了里面一些基因的坐标,就导致里面的translation这一栏跟坐标对不上,需要更新一下。虽然我有能力写这个代码去更新结果,但是我希望给GPT(模型turbo 3.5)一个机会,让他处理下。
首先,我问了它关于genbank的格式定义,确保它后续能够进行处理。他的回答非常正确,符合我的认知(下面是对话截图)

接下来我就开始问问题了,我让他编写脚本,让我调整坐标,它写了一段python 的代码,通过调用BioPython模块来实现我刚才说的功能。

但是这代码有问题,因为通用性比较差,所以我让他改写代码,有一个遍历过程,先得到新的CDS,然后和原来的translation进行比较,如果存在不同则替换
它的工作非常棒,下面是它给的结果。
from Bio import SeqIO
# 读取GenBank文件
record = SeqIO.read("your_genbank_file.gb", "genbank")
# 遍历所有CDS区域
for feature in record.features:
if feature.type == "CDS":
# 获取原始位置信息
old_start = feature.location.start
old_end = feature.location.end
# 修改位置信息为新的位置
new_start = 100 # 新的起始位置
new_end = 500 # 新的终止位置
feature.location = feature.location._shifted(new_start - old_start)
feature.location = feature.location._shifted(new_end - old_end)
# 更新翻译信息
old_translation = feature.qualifiers.get("translation", [""])[0]
new_sequence = feature.extract(record.seq) # 提取新序列
new_translation = new_sequence.translate(to_stop=True) # 计算新的翻译信息
new_translation_str = str(new_translation)
if new_translation_str != old_translation:
feature.qualifiers["translation"] = [new_translation_str]
# 写回GenBank文件
with open("modified_genbank_file.gb", "w") as output_handle:
SeqIO.write(record, output_handle, "genbank")
不过它总是念念不忘他的new_start 和 new_ned,这显然不是我需要的,所以,我让他把这部分去掉。下面截图是我的提问和它的回答。
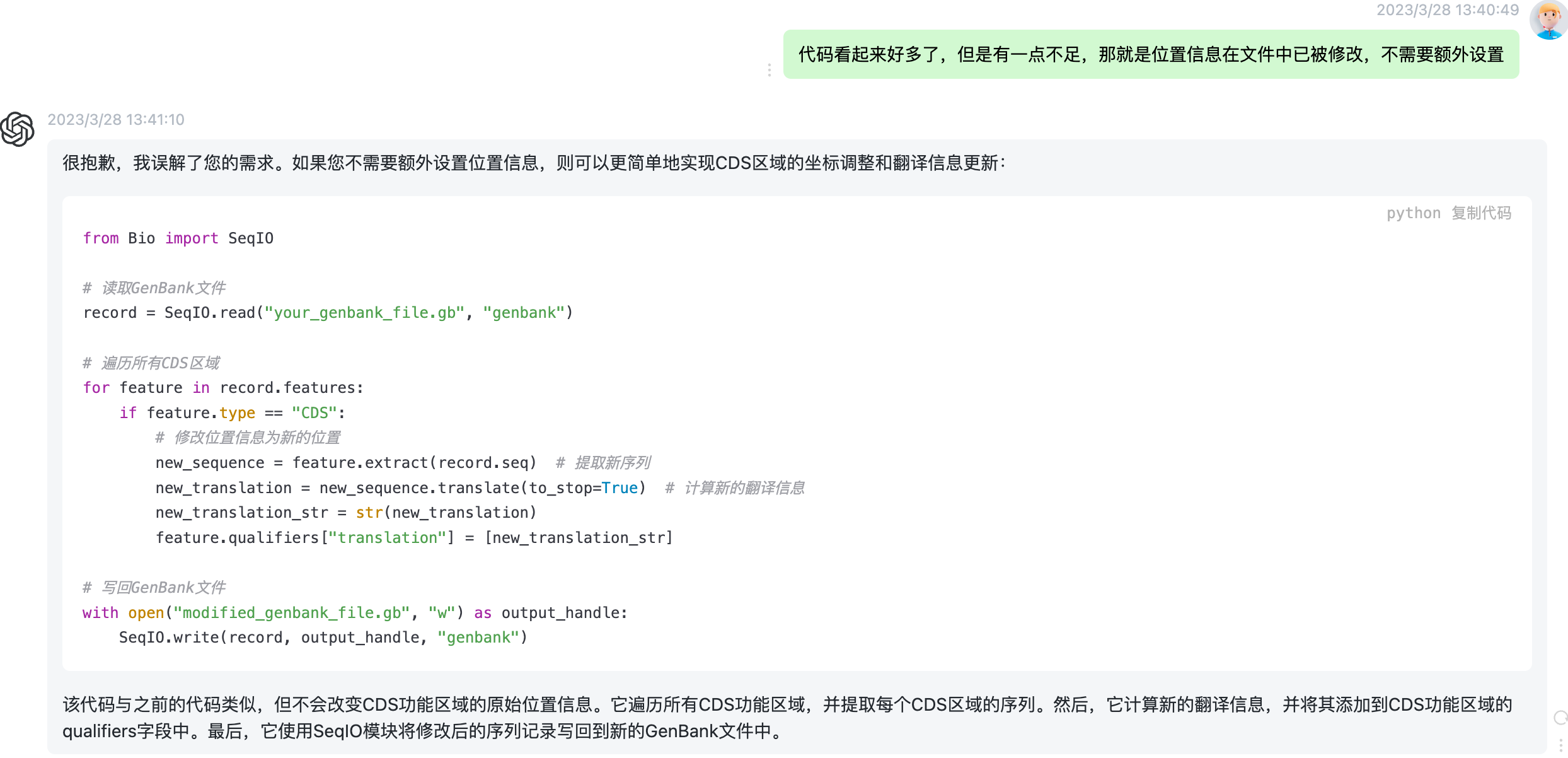
这次代码简洁多了。不过他还不是一个合格的代码,因为调用只能是固定的文件名,我希望它能进一步提高通用性,所以我的提问是“好的,进一步提供他的通用性,使得我们可以在命令行通过 python remake.py input.gb output.gb来实现文件的重新生成”
这次他的回答更加的棒,它用了argparse模块,并将原来的代码函数化,下面是他的回答。
import argparse
from Bio import SeqIO
def update_cds_translation(record, new_positions):
"""
更新GenBank记录中所有CDS区域的翻译信息并返回修改后的记录。
:param record: GenBank记录对象
:param new_positions: 包含每个CDS区域新起始和终止位置的dict对象
:return: 修改后的GenBank记录对象
"""
for feature in record.features:
if feature.type == "CDS":
# 获取CDS区域原始序列和翻译信息
old_sequence = feature.extract(record.seq)
old_translation = feature.qualifiers.get("translation", [""])[0]
# 获取CDS区域新位置
start, end = new_positions.get(feature.qualifiers['gene'][0], (feature.location.start, feature.location.end))
# 调整CDS区域位置并计算新翻译信息
feature.location = feature.location._shifted(start - feature.location.start)
feature.location = feature.location._shifted(end - feature.location.end)
new_sequence = feature.extract(record.seq)
new_translation = new_sequence.translate(to_stop=True)
new_translation_str = str(new_translation)
# 如果翻译信息不同,则更新qualifiers字段
if new_translation_str != old_translation:
feature.qualifiers["translation"] = [new_translation_str]
return record
if __name__ == '__main__':
# 解析命令行参数
parser = argparse.ArgumentParser(description="Update CDS translations in a GenBank file.")
parser.add_argument("input", help="Input GenBank file name")
parser.add_argument("output", help="Output GenBank file name")
parser.add_argument("-p", "--positions", help="New start and end positions for each gene, e.g. 'gene1:100-500 gene2:200-600'", default="")
args = parser.parse_args()
# 读取GenBank文件和新位置信息
record = SeqIO.read(args.input, "genbank")
new_positions = {gene_pos.split(":")[0]: tuple(map(int, gene_pos.split(":")[1].split("-"))) for gene_pos in args.positions.strip().split()}
# 更新CDS翻译信息并写回GenBank文件
updated_record = update_cds_translation(record, new_positions)
with open(args.output, "w") as output_handle:
SeqIO.write(updated_record, output_handle, "genbank")
更惊喜的是,在它的解释中,它还扩展了功能,它说道
此代码使用argparse模块解析命令行参数,并根据提供的输入文件名和输出文件名读取和写入GenBank记录。它还允许通过命令行参数-p/--positions指定每个基因的新起始和终止位置,方式为'gene1:100-500 gene2:200-600'。如果不提供此参数,则使用每个CDS区域的原始位置。最后,它调用update_cds_translation函数来更新所有CDS区域的翻译信息,然后将修改后的GenBank记录写回到输出文件中。
我觉得差不多了,并复制了代码,开始运行,然后我报错了。错误信息如下
我运行了代码,出现了如下报错,我应该如何处理
Traceback (most recent call last):
File "/Users/xuzhougeng/Downloads/remake.py", line 48, in <module>
updated_record = update_cds_translation(record, new_positions)
File "/Users/xuzhougeng/Downloads/remake.py", line 22, in update_cds_translation
feature.location = feature.location._shifted(start - feature.location.start)
AttributeError: 'FeatureLocation' object has no attribute '_shifted'
我直接复制了这段代码,问gpt怎么办,它推断是biopython的版本问题,还给我写了一个更加通用的代码,新的代码如下
import argparse
from Bio import SeqIO, SeqFeature
def update_cds_translation(record, new_positions):
"""
更新GenBank记录中所有CDS区域的翻译信息并返回修改后的记录。
:param record: GenBank记录对象
:param new_positions: 包含每个CDS区域新起始和终止位置的dict对象
:return: 修改后的GenBank记录对象
"""
for feature in record.features:
if feature.type == "CDS":
# 获取CDS区域原始序列和翻译信息
old_sequence = feature.extract(record.seq)
old_translation = feature.qualifiers.get("translation", [""])[0]
# 获取CDS区域新位置
start, end = new_positions.get(feature.qualifiers['gene'][0], (feature.location.start, feature.location.end))
# 调整CDS区域位置并计算新翻译信息
offset_start = start - feature.location.start
offset_end = end - feature.location.end
new_location = SeqFeature.FeatureLocation(
feature.location.start + offset_start,
feature.location.end + offset_end,
feature.location.strand
)
new_sequence = feature.extract(record.seq)
new_translation = new_sequence.translate(to_stop=True)
new_translation_str = str(new_translation)
# 如果翻译信息不同,则更新qualifiers字段
if new_translation_str != old_translation:
feature.qualifiers["translation"] = [new_translation_str]
# 更新位置信息
feature.location = new_location
return record
if __name__ == '__main__':
# 解析命令行参数
parser = argparse.ArgumentParser(description="Update CDS translations in a GenBank file.")
parser.add_argument("input", help="Input GenBank file name")
parser.add_argument("output", help="Output GenBank file name")
parser.add_argument("-p", "--positions", help="New start and end positions for each gene, e.g. 'gene1:100-500 gene2:200-600'", default="")
args = parser.parse_args()
# 读取GenBank文件和新位置信息
record = SeqIO.read(args.input, "genbank")
new_positions = {gene_pos.split(":")[0]: tuple(map(int, gene_pos.split(":")[1].split("-"))) for gene_pos in args.positions.strip().split()}
# 更新CDS翻译信息并写回GenBank文件
updated_record = update_cds_translation(record, new_positions)
with open(args.output, "w") as output_handle:
SeqIO.write(updated_record, output_handle, "genbank")
这个代码对不对呢?至少我跑完是没有报错的,我进一步的检查了它的分析结果。发现很多CDS的长度明显短了,我觉得这可能是我没有说清楚,我给的是线粒体基因组。我讲这个结果反馈给了gpt,它认可了我的推测,下面是他的回答。

后来我们又反反复复商量了好几轮,对代码反复打磨,通常都是它给出了建议,我询问他是不是有另一种解决思路,比如说有些genbank文件里的cds长度有问题,不一定是3的倍数,他建议我对处理来的文件,我觉得可以考虑捕获报错,他也执行的特别好。
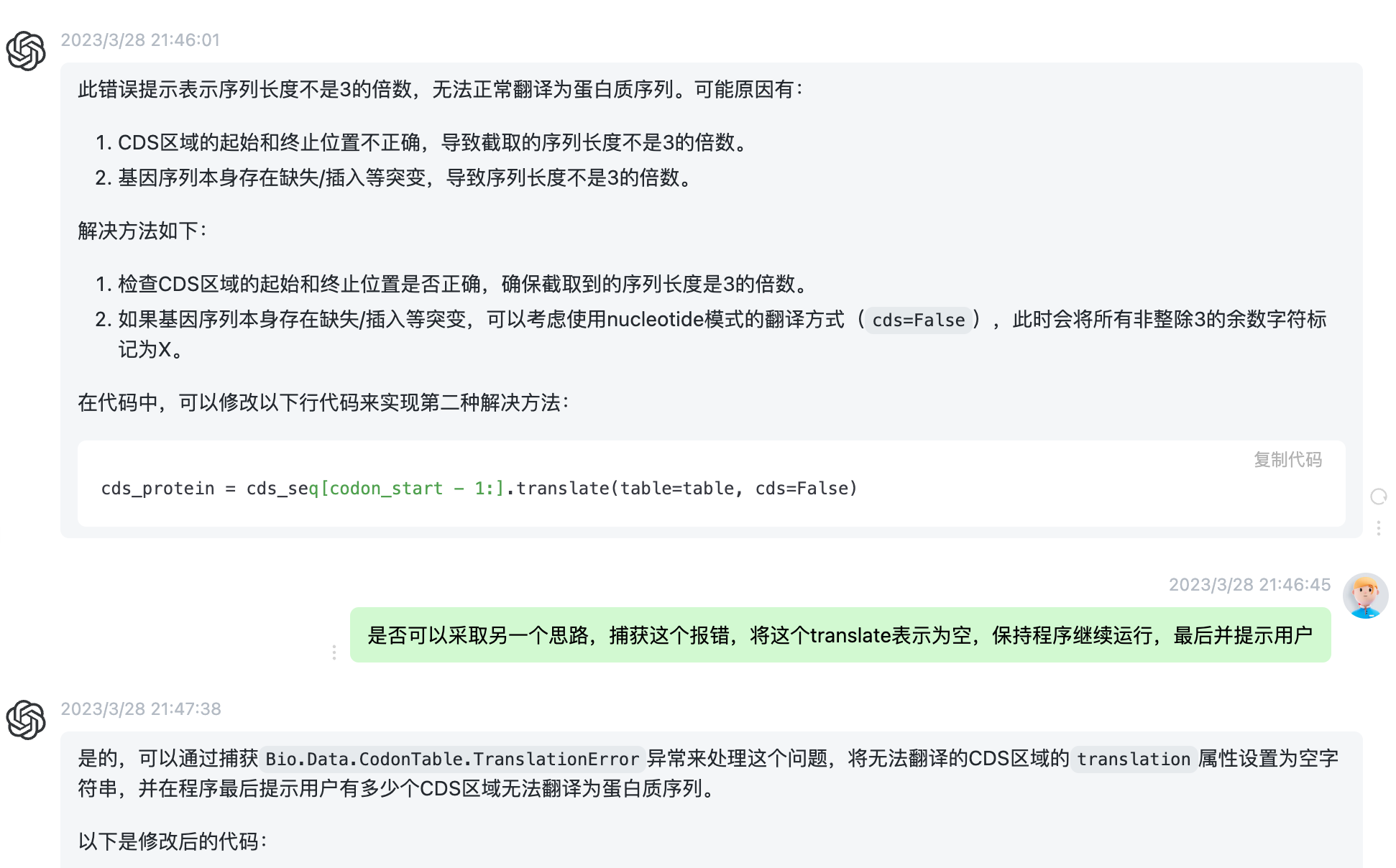
下面的代码目前我最为满意的版本了
import argparse
from Bio import SeqIO, Data
def update_cds_translation(record, new_positions):
"""
更新GenBank记录中所有CDS区域的翻译信息并返回修改后的记录。
:param record: GenBank记录对象
:param new_positions: 包含每个CDS区域新起始和终止位置的dict对象
:return: 修改后的GenBank记录对象
"""
# 遍历每个特征
for feature in record.features:
# 如果是CDS区域
if feature.type == 'CDS':
# 获取特征的名称
gene = feature.qualifiers.get('gene', [''])[0]
# 获取CDS区域的起始和终止位置
start, end = feature.location.start, feature.location.end
# 如果有新位置信息,则使用新位置信息
if gene in new_positions:
start, end = new_positions[gene]
# 获取CDS区域的序列
cds_seq = record.seq[start:end]
# 判断序列的方向
if feature.strand == -1:
cds_seq = cds_seq.reverse_complement()
# 获取codon_start和transl_table信息
codon_start = int(feature.qualifiers.get('codon_start', [1])[0])
transl_table = int(feature.qualifiers.get('transl_table', [1])[0])
# 翻译CDS区域
table = Data.CodonTable.unambiguous_dna_by_id[transl_table]
try:
cds_protein = cds_seq[codon_start - 1:].translate(table=table, cds=True)
except Data.CodonTable.TranslationError:
cds_protein = ''
print(f"Warning: Unable to translate CDS region {gene} in record {record.id}")
# 更新CDS区域的翻译信息
feature.qualifiers['translation'] = [str(cds_protein)]
return record
if __name__ == '__main__':
# 解析命令行参数
parser = argparse.ArgumentParser(description="Update CDS translations in a GenBank file.")
parser.add_argument("input", help="Input GenBank file name", type=argparse.FileType('r'))
parser.add_argument("output", help="Output GenBank file name", type=argparse.FileType('w'))
parser.add_argument("-p", "--positions", help="New start and end positions for each gene, e.g. 'gene1:100-500 gene2:200-600'", default="")
args = parser.parse_args()
# 读取GenBank文件和新位置信息
records = (record for record in SeqIO.parse(args.input, "genbank"))
new_positions = {gene: tuple(map(int, pos.split('-'))) for gene, _, pos in map(str.partition, args.positions.split())}
# 更新CDS翻译信息并写回GenBank文件
untranslated_cds_count = 0
for record in records:
record = update_cds_translation(record, new_positions)
# 统计无法翻译的CDS区域个数
for feature in record.features:
if feature.type == 'CDS' and not feature.qualifiers.get('translation', [''])[0]:
untranslated_cds_count += 1
SeqIO.write(record, args.output, "genbank")
# 提示用户有多少个CDS区域无法翻译为蛋白质序列
if untranslated_cds_count > 0:
print(f"Warning: Failed to translate {untranslated_cds_count} CDS regions.")
我运行了这个代码,发现结果非常好。
$ python remake.py mitoscaf.fa.gbf new.gff
Warning: Unable to translate CDS region COX2 in record XZG
Warning: Failed to translate 1 CDS regions.
其实早在几年前,openAI推出GPT3的时候,我就知道了,我也提交了申请,但是一直没被通过,也就被我忘了。后来chatGPT横空出世,我开始也聊了几句,后面也就放在一边了。直到最近,它又火了,并且还出现了一个非常优秀的github项目,chatgpt-web,使得我能搭建了一个自己的专属GPT,之后我还搞定了付费API。
虽然他也会出错(未来的4.0 API或许会好很多),但这样子说的仿佛人不出错一样。我现在就把它当做一个合作搭档,我有一个想法,让我帮我快速实现一下,然后我根据结果进行修改,并反馈给他,他也能迅速的给我一个反馈,这不挺好吗?
