用C写一个链表
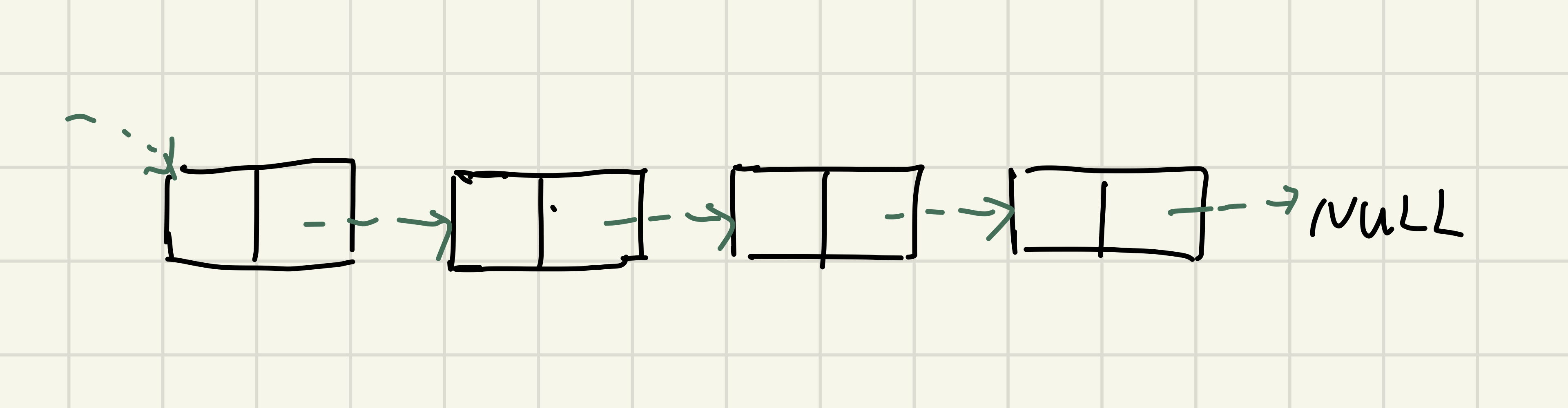
链表(Linked List)是一种非连续的线性数据结构,相对于数组,它允许数据在内存中非连续存储,但是不支持随机读取。

链表由一个个节点(Node)组成,每个节点除了记录数据以外,还需要记录下一个节点的位置(如果是双向链表,还需要记录上一个节点的位置)
struct _Node;
typedef struct _Node Node;
struct _Node{
int data; //记录整型数据
Node *next;
};
对于第一个节点,我们有一个指针指向它的地址,对于最后一个节点,它需要指向NULL,表示链表结束了。
typedef struct _List {
Node *head; //记录头地址
Node *tail; //记录尾巴地址
int num;
} List;
有了链表的数据结构后,我们需要定义三个基本函数,用于创建链表,往链表中加入数据和删除链表
创建链表比较简单,就是为链表分配内存,并将其赋值给一个指针,然后返回
// 创建链表
List *CreateList()
{
List *list;
list = (List*)malloc( sizeof(List) );
list->num = 0;
return list;
}
加入数据时,我们需要先声明两个节点指针,第一个用于记录当前节点的位置,第二个是记录新节点的位置。如果链表中没有节点,也就是head指向为NULL,那么直接插入新节点即可。如果链表中已经有了节点,那么获取最后第一个节点的位置, 然后在它的后面加入节点,同时将tail指向新的节点。
bool AddNode(List *list, int data)
{
Node *node;
Node *new_node;
new_node = (Node *)malloc( sizeof(Node) );
if ( new_node == NULL) return false;
new_node->data = data;
new_node->next = NULL;
//获取链表head
node = list->head ;
//如果head指向NULL, 则直接插入到下一个
if ( node == NULL){
list->head = new_node;
list->tail = new_node;
list->num = 1;
return true;
}
// 否则在尾部插入节点
node = list->tail ;
node->next = new_node;
list->tail = new_node;
list->num+=1;
return true;
}
删除列表分为两步,先删除节点内容,然后删除列表这个结构。如果节点存放的数据是其他结构,那么还需要先删除节点存放的其他数据。
void DestroyList(List *list)
{
Node *current;
Node *next;
current = list->head;
while (current->next != NULL){
next = current->next;
free(current);
current = next;
}
free(list);
}
我们还可以定一个输出函数,将链表里存放的数据依次输出
//打印整个链表
void dump(List *list){
Node *node;
node = list->head;
while (node != NULL){
printf("%08d\n", node->data);
node = node->next;
}
}
有了上面的基本函数时候,我们就能够读取存放数字的文本,将其加入到链表中。
int main(int argc, char const *argv[])
{
/* code */
if (argc == 1) exit(EXIT_FAILURE);
FILE *fp;
fp = fopen(argv[1], "r");
if (fp == NULL){
perror(argv[1]);
exit(EXIT_FAILURE);
}
int data;
List *list;
list = CreateList();
while (fscanf(fp, "%d", &data) != EOF){
AddNode(list, data);
}
dump(list)
return 0;
我们的链表还应该支持插入操作和删除操作。对于插入操作,我们要分为是插入到给定位置前,还是给定位置后。对于删除而言,也就是都是删除当前节点,而为了删除当前节点,我们需要前一个节点的位置。
无论是插入还是删除,我们都需要知道插入的位置和删除的位置,因此我们还需要一个搜索函数,用于搜索等于给定值的节点位置或者是上一个位置。
// 查找元素
// situ=true时, 返回当前位置, false, 则返回上一个位置
Node *Search(List *list, int data, bool situ)
{
Node *node;
node = list->head;
if ( situ ){
while ( node->next != NULL ){
if ( node->data == data)
return node;
node = node->next;
}
} else {
while ( node->next->next != NULL) {
if (node->next->data == data)
return node;
node = node->next;
}
}
return NULL;
}
我们先写一个删除操作, 用于删除等于给定的节点。
//删除节点
bool DeleteNode( List* list, int data){
Node *node;
Node *tmp;
node = list->head;
// 判断这个节点是否是首节点
if ( node->data == data ){
free(list->head);
list->head = NULL;
list->tail = list->head;
list->num = 0;
return true;
}
// 查找给定节点的前一个节点
node = Search(list, data, false);
// 找不到节点
if ( node == NULL){
return false;
}
//删除
tmp = node->next->next;
free(node->next);
node->next = tmp;
return true;
}
然后将元素加入函数分为两种,一种是插入(当前位置前),一种是追加(当前位置后)
//在给定元素前加节点
bool InsertNode( List* list, int query, int data){
Node *node;
Node *new_node;
// 为新节点分配内存
new_node = (Node *)malloc( sizeof(Node) );
if ( new_node == NULL) return false;
new_node->data = data;
node = list->head;
// 判断这个节点是否是首节点
if ( node->data == query ){
new_node->next = node->next ;
node->next = new_node;
return true;
}
// 查找给定节点的前一个节点
node = Search(list, query, false);
// 找不到节点
if ( node == NULL){
return false;
}
new_node->next = node->next ;
node->next = new_node;
return true;
}
//在给定元素后加
bool AppendNode( List* list, int query, int data){
Node *node;
Node *new_node;
// 为新节点分配内存
new_node = (Node *)malloc( sizeof(Node) );
if ( new_node == NULL) return false;
new_node->data = data;
// 查找给定节点的位置
node = Search(list, query, true);
// 找不到节点
if ( node == NULL){
return false;
}
new_node->next = node->next;
node->next = new_node;
return true;
}
进阶操作
上面都是链表的基础操作,创建、摧毁,增加,删除。下面几个则是考验对链表对深刻理解,
- 单链表反转
- 链表中环的检测
- 两个有序链表的合并
- 删除链表倒数第N个结点
- 求链表的中间结点
单链表反转
如果要将单链表进行反转,每次移动的时候需要三个位置,前一个位置,当前位置和head。每次将head向后移动,记录了当前位置的下一个节点,然后将当前位置指向前一个位置。最后将前一个位置和当前位置向后移动。图解如下, 首先head指向链表第一个节点

然后将cur设置到当前的head

接着将head往后移动一个位置, 保存了原本在cur后面的位置

然后将cur指向到res,也就是前面的位置

上面的操作后,就将res和cur的顺序反转了。接着就是将res和cur往后移动

代码为
List* reverseList(List* list){
Node *curr, *res;
res = NULL;
curr = list->head;
//尾巴是之前的开头
list->tail = list->head;
while ( curr ){
//移动head
list->head = list->head->next;
//将当前位置指向前一个位置
curr->next = res;
//依次向后移动res和curr
res = curr;
curr = list->head;
}
list->head = res;
return list;
}
中间节点
为了寻找中间节点,我们可以定义两个指针,快指针和慢指针。慢指针一次一步,快指针一次两步. 如果是偶数,那么快指针最后是NULL,如果是奇数,那么快指针的下一个是NULL。
Node *FindMidlle(List *list)
{
if (list->num == 0) return NULL;
Node *fast = list->head;
Node *slow = list->head;
while ( fast != NULL && fast->next != NULL){
slow = slow->next;
fast = fast->next->next;
}
return slow;
}
删除倒数第N个指针
同上,也是快慢两个指针,快指针先走N步,然后两个指针再一起走。
bool RemoveLastN(List *list, int n)
{
//删除第一个
if ( list->num == n){
list->head = list->head->next;
return true;
}
Node *fast = list->head;
Node *slow = list->head;
Node *tmp;
while (n-- > 0){
fast = fast->next;
}
while (fast->next != NULL){
fast = fast->next;
slow = slow->next;
}
tmp = slow->next;
slow->next = slow->next->next;
free(tmp);
return true;
}
有序链表合并
假设两个有序链表分别为1->3->5->7->8,2->3->4->5->8, 那么合并之后应该是1->2->3->3->4->5->7->8.
我们需要创建一个新的链表用于存放两个链表排序的结果
//合并两个链表
List *MergeSortedList(List *list_a, List *list_b)
{
List *list_c;
list_c = CreateList();
Node *node_a, *node_b, *node_c;
node_a = list_a->head;
node_b = list_b->head;
//确定新列表的head
if ( node_a->data < node_b->data ){
list_c->head = node_a;
node_a = node_a->next;
} else {
list_c->head = node_b;
node_b = node_b->next;
}
node_c = list_c->head;
while( true ){
if (node_a->data < node_b->data){
node_c->next = node_a;
node_a = node_a->next;
if (node_a == NULL) break;
} else{
node_c->next = node_b;
node_b = node_b->next;
if (node_b == NULL) break;
}
node_c = node_c->next;
}
while ( node_a != NULL){
node_c->next = node_a;
node_a = node_a->next;
node_c = node_c->next;
}
while ( node_b != NULL){
node_c->next = node_b;
node_b = node_b->next;
node_c = node_c->next;
}
return list_c;
}
为了测试这个代码正确性,我写了一个测试函数
int MergeTest( const char *file1, const char *file2){
FILE *f1;
FILE *f2;
int data;
f1 = fopen(file1, "r");
List *list1;
list1 = CreateList();
//读取数据
while (fscanf(f1, "%d", &data) != EOF){
AddNode(list1, data);
}
dump(list1);
fclose(f1);
f2 = fopen(file2, "r");
if (f2 == NULL){
perror(file2);
exit(EXIT_FAILURE);
}
List *list2;
list2 = CreateList();
//读取数据
while (fscanf(f2, "%d", &data) != EOF){
AddNode(list2, data);
}
dump(list2);
fclose(f2);
List *res;
res = MergeSortedList(list1, list2);
dump(res);
return 0;
}
最终的代码在GitHub上https://github.com/xuzhougeng/learn-algo/blob/master/link_list.c
LeetCode和链表有关的几个题目